What Causes Insanely Loud Snoring?
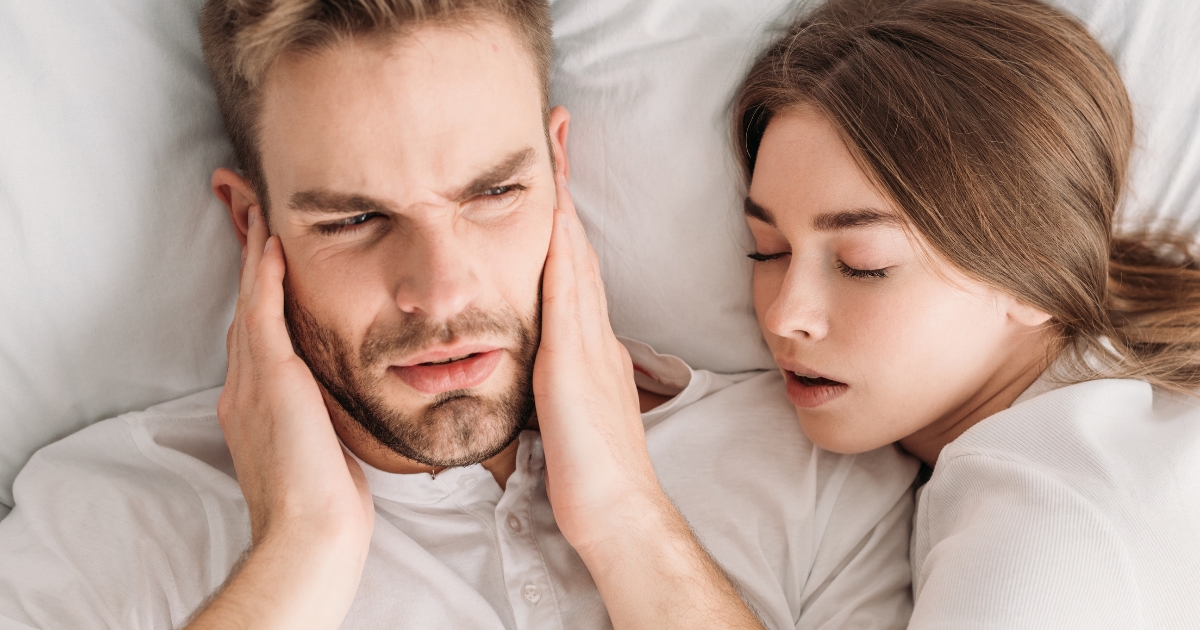

Snoring isn’t just a minor inconvenience; for many, it’s an all-night concert they never requested. It can disrupt sleep, cause fatigue, and even strain relationships. But what’s behind that thunderous noise? Let’s dive into the causes of loud snoring and how you can quiet the storm for good.
1. Obstructed Airways: The Most Common Culprit
The sound of snoring often begins with an obstruction in the airway. When air can’t flow smoothly through your nose or throat during sleep, the tissues around the airway vibrate, producing that familiar sound. It’s like a wind instrument—narrow passages amplify the noise. Various factors can block airflow, from nasal congestion to swollen tonsils. Even something as simple as a cold can turn your peaceful night into a noisy one.
Chronic allergies or a deviated septum can contribute to more persistent snoring for some. If you wake up with a stuffy nose or dry mouth, it could indicate that your airways are struggling to stay open.
2. The Role of Sleep Position
Ever notice how some people snore louder when they’re on their back? That’s because lying flat allows the tongue to fall backward, partially blocking the throat. Sleeping on your side often reduces snoring, as it helps keep the airway open. While it’s not a foolproof solution, many have found relief by shifting positions.
A helpful tip: try using a body pillow or placing a tennis ball behind your back to encourage side-sleeping. It sounds strange, but for some, it works like a charm.
3. Weight and Snoring: Is There a Link?
Carrying extra weight, especially around the neck, can increase the likelihood of snoring. Excess tissue can press against the throat, making it harder for air to pass through smoothly. This is why snoring tends to be more common in overweight people.
Losing even a small amount of weight can sometimes reduce snoring. However, it’s worth noting that this isn’t a universal fix. Plenty of slim individuals also snore, so weight loss alone may not be the sole solution.
4. Alcohol and Sedatives: A Recipe for Snoring
Have you had a couple of drinks before bed? Alcohol can relax the muscles in your throat, making it more likely for those tissues to collapse and block airflow. Similarly, sedatives and sleep aids can have the same effect. While these substances might make you feel relaxed, they can also turn a quiet sleeper into a loud snorer.
If you’re looking to reduce snoring, try cutting out alcohol a few hours before bedtime. You might find that it makes a noticeable difference.
5. Sleep Apnea: More Than Just Snoring
Not all snoring is created equal. For some, loud snoring could signal a more severe issue: sleep apnea. This condition occurs when your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. These pauses can last several seconds, causing a sharp gasp or snort as your body wakes you up to breathe. People with sleep apnea often experience loud snoring, daytime fatigue, and frequent awakenings.
If you suspect sleep apnea, seeking sleep apnea treatment is crucial. Untreated, this condition can lead to a host of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and more. Treatments range from lifestyle changes, like weight loss, to using a CPAP machine, which helps keep your airways open while you sleep. Don’t ignore the signs; addressing sleep apnea can improve your quality of life.
6. The Anatomy of Your Airway
Some people are more prone to snoring due to their anatomy. You may be more likely to snore if you have a long uvula (the dangly thing at the back of your throat) or an unusually narrow airway. Enlarged tonsils or adenoids can also block airflow, especially in children.
While we can’t control our anatomy, surgical options are available for those who snore due to structural issues. Removing the tonsils or adjusting the soft palate may relieve more severe cases.
7. Age and Snoring: It Gets Worse with Time
Getting older comes with its fair share of challenges, and snoring is one of them. As we age, the muscles in our throats tend to lose tone, making them more likely to collapse during sleep. This loss of muscle tone can lead to louder, more frequent snoring.
Unfortunately, there’s no stopping the clock, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying active, and managing weight can help reduce age-related snoring.
8. Nasal Problems: Breathe Easy
Your nose plays a significant role in snoring. You may be more prone to snoring if your nasal passages are clogged due to allergies, colds, or sinus issues. Chronic nasal congestion forces you to breathe through your mouth, which increases the chance of loud, persistent snoring.
If allergies are a trigger, managing them with over-the-counter remedies or consulting a doctor for long-term solutions can help. Nasal strips or dilators can also provide temporary relief by helping to open the nasal passages during sleep.
9. Hormonal Changes and Snoring in Women
Interestingly, women may experience more frequent snoring during certain life stages, particularly during pregnancy or menopause. Hormonal shifts can cause weight gain, fluid retention, and other changes that increase the likelihood of snoring.
Snoring often resolves after childbirth for pregnant women. However, if it’s persistent, it’s worth discussing with a healthcare provider to rule out more serious conditions like sleep apnea.
10. How to Address Loud Snoring
While some snoring causes are temporary, others may require long-term solutions. Here are a few strategies to reduce snoring:
- Change Sleep Positions: Sleep on your side to keep the airway open.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a little weight can help reduce snoring for some.
- Avoid Alcohol Before Bed: Cut back on alcohol, especially in the evening, to avoid airway relaxation.
- Treat Nasal Congestion: Keep your nasal passages clear to encourage easy breathing.
- Consider Sleep Apnea Treatment: If snoring is paired with gasping or choking, consult a doctor for a sleep study and possible Sleep Apnea treatment.
Snoring doesn’t have to be a permanent fixture in your life. Understanding what causes snoring is the first step in finding relief. Whether adjusting your sleep position, losing weight, or seeking sleep apnea treatment, there are ways to quiet the noise and get back to restful sleep. For those struggling with chronic snoring, don’t hesitate to contact a sleep apnea specialist or treatment center. You and your bed partner will thank you for it!